The Science Behind Extreme Weather: A 2025 Analysis in the US

The Science Behind the Recent Increase in Extreme Weather Events Across the US: A 2025 Analysis reveals a complex interplay of climate change drivers, intensified by factors such as greenhouse gas emissions and altered atmospheric patterns, leading to more frequent and severe weather phenomena.
The stories are increasingly common: devastating floods, record-breaking heat waves, and ever-stronger hurricanes. Extreme weather events across the US are on the rise, leaving communities reeling and scientists searching for answers. What’s driving this alarming trend? This article delves into the science behind the recent increase in extreme weather events across the US: A 2025 analysis, exploring the factors contributing to this growing crisis.
Understanding the complex interactions within our climate system is crucial to predicting and mitigating the impacts of these events. We’ll examine the role of climate change, atmospheric patterns, and human activities in shaping the future of American weather. Are we prepared for what’s to come? Read on to discover the science behind these changes.
Understanding Climate Change and Extreme Weather in the US
The connection between climate change and the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather is a central point of scientific inquiry. Rising global temperatures, driven by greenhouse gas emissions, are altering the fundamental dynamics of the Earth’s climate system. This section explores how these changes translate into specific weather phenomena across the United States.
The Role of Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, trap heat in the atmosphere. The increased concentration of these gases is primarily due to human activities, including the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation. This trapped heat raises global temperatures, leading to a cascade of effects on weather patterns.
Observed Temperature Increases in the US
The US has experienced a significant warming trend over the past several decades. According to the National Climate Assessment, average temperatures have risen by 1.3°F to 1.9°F since 1895, with the most recent decade being the warmest on record. These increases are not uniform across the country, with some regions experiencing more pronounced warming than others. These observed impacts contribute greatly to the science behind the recent increase in extreme weather events across the US: A 2025 analysis.
- Heat Waves: More frequent and intense heat waves are becoming commonplace, straining infrastructure and posing health risks.
- Sea Level Rise: Coastal communities are facing increased flooding and erosion due to rising sea levels.
- Changes in Precipitation: Some regions are experiencing increased rainfall and flooding, while others are grappling with prolonged droughts.
In summary, climate change, driven by greenhouse gas emissions and resulting in observed temperature increases throughout the United States, are heavily attributed to the more frequent and intense extreme weather. Rising global temperatures alter the Earth’s climate system and dramatically affect weather patterns.
Changes in Atmospheric Patterns and Their Impact
Beyond overall temperature increases, shifts in atmospheric patterns are playing a crucial role in the surge of extreme weather events. These patterns influence where and how weather systems develop and evolve, contributing to both the occurrence and severity of events.
The Jet Stream and Extreme Weather
The jet stream, a high-altitude wind current, plays a critical role in steering weather systems across North America. As the Arctic warms, the temperature difference between the Arctic and lower latitudes decreases, weakening the jet stream. This weakening can lead to a more undulating, meandering jet stream pattern.
Blocking Patterns and Stalled Weather Systems
A wavier jet stream is more prone to forming “blocking patterns,” where high-pressure systems become stationary for extended periods. These blocking patterns can cause weather systems to stall, leading to prolonged droughts, heat waves, or heavy rainfall events in the affected areas.
- Prolonged Heat Waves: Blocking patterns can trap hot air masses over a region, leading to extended periods of extreme heat.
- Increased Flooding: Stalled weather systems can dump massive amounts of rainfall on localized areas, causing severe flooding.
- Drought Conditions: Conversely, blocking patterns can also prevent rainfall from reaching certain areas, exacerbating drought conditions.
Ultimately, changes in atmospheric patterns, which greatly include the meandering jet stream, are critical to the science behind the recent increase in extreme weather events across the US: A 2025 analysis. An undulating jet stream is more prone to create blocking patterns, resulting in stalled weather systems.
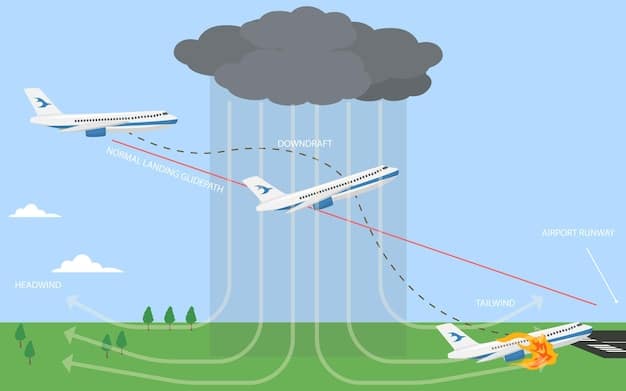
The Science Behind Extreme Precipitation and Flooding
Many parts of the US have seen an increase in heavy precipitation events, leading to more frequent and severe flooding. Understanding the dynamics that contribute to these events is crucial for effective risk management and adaptation strategies.
Increased Atmospheric Moisture
Warmer air can hold more moisture, meaning that storms have the potential to unleash far greater amounts of rainfall. This increased atmospheric moisture is a direct consequence of rising global temperatures. Warmer temperatures translate to storms that are far stronger.
Urbanization and Runoff
The expansion of urban areas, with their vast expanses of impervious surfaces like concrete and asphalt, exacerbates the risk of flooding. These surfaces prevent rainwater from soaking into the ground, leading to rapid runoff and overwhelmed drainage systems. The effects of urbanization directly impact the science behind the recent increase in extreme weather events across the US: A 2025 analysis.
- Infrastructure Vulnerability: Aging and inadequate infrastructure struggles to handle the increased volume of stormwater, contributing to flooding.
- Land Use Practices: Deforestation and unsustainable agricultural practices can reduce the land’s capacity to absorb water, increasing runoff.
- Coastal Flooding: Rising sea levels combined with storm surges intensify coastal flooding, threatening coastal communities.
To summarize, increased atmospheric moisture coupled with urbanization and resulting runoff dramatically affects the science behind extreme precipitation and flooding. With the expansion of urban areas, drainage systems are often overwhelmed, causing stormwater to rapidly intensify throughout the US.
The Impact of Extreme Heat Waves and Droughts
While some regions grapple with increased flooding, others are facing more frequent and intense heat waves and droughts. These events pose significant risks to human health, agriculture, and ecosystems. As a result, understanding their causes and impacts is paramount to protecting the population and environment.
The Connection Between Heat Waves and Climate Change
Rising global temperatures are directly linked to the increased frequency and intensity of heat waves. As average temperatures rise, the likelihood of experiencing prolonged periods of extreme heat increases. This directly impacts the frequency and effects of heat waves throughout the United States.
Droughts and Water Scarcity
Prolonged periods of drought can lead to water scarcity, impacting agriculture, municipal water supplies, and ecosystems. Droughts can also increase the risk of wildfires and dust storms.

- Heat-Related Illnesses and Deaths: Extreme heat can overwhelm the body’s ability to regulate temperature, leading to heatstroke and other heat-related illnesses.
- Agricultural Losses: Droughts can devastate crops and livestock, leading to economic losses and food insecurity.
- Ecosystem Impacts: Droughts can stress ecosystems, leading to tree mortality, reduced biodiversity, and increased wildfire risk.
Extreme heat waves coupled with droughts are having a lasting and detrimental effect on ecosystems, agriculture, livestock, and municipal water supplies. When these patterns persist, we are left with significant impacts on the health of populations and the environment.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Extreme Weather
Addressing the challenge of extreme weather requires a two-pronged approach: mitigating climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adapting to the inevitable impacts of a changing climate. Both approaches are essential for protecting communities and minimizing the damage from future extreme weather events.
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The most fundamental step in mitigating extreme weather is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This requires a transition to cleaner energy sources, increased energy efficiency, and sustainable land use practices.
Investing in Resilient Infrastructure
Adapting to extreme weather requires investing in infrastructure that can withstand the impacts of these events. This includes upgrading drainage systems, building seawalls, and reinforcing power grids. Investing in such infrastructure is critical to preparing for the more intense and frequent extreme weather events.
- Early Warning Systems: Implementing advanced weather forecasting and early warning systems can provide communities with timely information to prepare for extreme weather events.
- Community Preparedness: Educating the public about the risks of extreme weather and providing resources for preparedness can help minimize the impacts of these events.
- Policy and Regulation: Implementing policies and regulations that promote climate resilience and reduce vulnerability to extreme weather is essential for long-term protection.
Ultimately, mitigating the factors of climate change and investing in more resilient infrastructure are key in addressing the challenge associated with the recent increase in extreme weather events. Early warning systems, as well as advanced weather forecasting, are important preparedness steps.
The Future of Extreme Weather in the US: A 2025 Outlook
Looking ahead to 2025, the scientific consensus suggests that extreme weather events will continue to increase in frequency and intensity across the US. Understanding the likely trends and potential impacts is crucial for proactive planning and adaptation. The science behind the recent increase in extreme weather events across the US: A 2025 analysis points to troubling scenarios.
Projected Increases in Heat Waves and Droughts
Many regions are projected to experience more frequent and intense heat waves and droughts. These events will likely strain water resources, increase wildfire risk, and pose significant health risks to vulnerable populations.
Increased Risk of Coastal Flooding
Coastal communities face a growing threat from rising sea levels and more intense coastal storms. This will result in more frequent and severe flooding, erosion, and infrastructure damage. These types of events demonstrate the science behind extreme weather patterns like increased risk of coastal flooding.
- Increased Wildfires: Drier conditions and higher temperatures will likely increase the risk of wildfires in many parts of the country.
- Disruptions to Agriculture: Extreme weather events will continue to disrupt agricultural production, leading to economic losses and food insecurity.
- Health Impacts: Extreme weather will continue to pose significant health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with pre-existing conditions.
In closing, projected increased risks in heat waves, droughts, coastal flooding and wildfires point to a troublesome outlook. The disruptions to agriculture and increased threats to public health demonstrate the real impact of the science behind the recent increase in extreme weather events across the US: A 2025 analysis.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🔥 Rising Temperatures | Increased heat waves impacting health. |
| 🌊 Coastal Flooding | Sea levels and potent storm patterns threaten coastlines. |
| 🌧️ Precipitation Increases | Increased rainfall with overwhelmed drainage systems. |
| 🌪️ Atmospheric Patterns | Weakened jet stream can stall weather systems. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Climate change, driven by increased greenhouse gas emissions, is the primary driver. Shifts in atmospheric patterns and urbanization also play significant roles.
A weaker jet stream becomes wavier, leading to blocking patterns that stall weather systems and prolong extreme conditions like heat waves or floods.
Building seawalls, upgrading drainage systems, and relocating infrastructure away from vulnerable coastal areas are adaptation measures to consider.
Individuals can reduce their carbon footprint, support policies that promote climate resilience, and prepare for extreme weather events through emergency planning.
Projections indicate a continued increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather, including heat waves, droughts, coastal flooding, and wildfires. This highlights the science behind the recent increase in extreme weather events across the US: A 2025 analysis.
Conclusion
The evidence is clear: extreme weather events are on the rise across the US, driven by a complex interplay of climate change, atmospheric shifts, and human activities. As this analysis of the science behind the recent increase in extreme weather events across the US: A 2025 analysis shows, understanding this is crucial for proactive mitigation.
By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, investing in resilient infrastructure, and empowering communities to prepare, we can mitigate the worst impacts and build a more sustainable future. The time to act is now, for the sake of our planet and future generations.





